- Published on
Implement Trie(Prefix Tree)
- Authors

- Name
- Alex Noh
Introduction
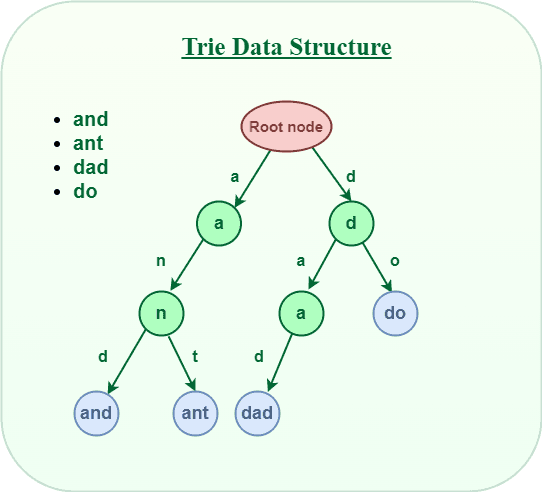
A trie (pronounced as "try") or prefix tree is a tree data structure used to efficiently store and retrieve keys in a dataset of strings. There are various applications of this data structure, such as autocomplete and spellchecker. Implement the Trie class.
Trie()Initializes the trie object.void insert(String word)Inserts the string word into the trie.boolean search(String word)Returns true if the string word is in the trie (i.e., was inserted before), and false otherwise.boolean startsWith(String prefix)Returns true if there is a previously inserted string word that has the prefix prefix, and false otherwise.
Solutions
Here is the implementation of a Trie data structure in Python. A Trie is a tree-like data structure that is used to efficiently store and retrieve keys in a dataset of strings. This implementation includes methods to insert words, search for a complete word, and check if any word in the Trie starts with a given prefix.
1. Implementing Trie
main.py
class TrieNode:
def __init__(self):
self.word = False
self.children = {}
class Trie:
def __init__(self):
self.root = TrieNode()
def insert(self, word: str) -> None:
node = self.root
for char in word:
if char not in node.children:
node.children[char] = TrieNode()
node = node.children[char]
node.word = True
def search(self, word: str) -> bool:
node = self.root
for char in word:
if char not in node.children:
return False
node = node.children[char]
return node.word
def startsWith(self, prefix: str) -> bool:
node = self.root
for char in prefix:
if char not in node.children:
return False
node = node.children[char]
return True