- Published on
Serialize & Deserialize Binary Tree
- Authors

- Name
- Alex Noh
Introduction
Serialization is the process of converting a data structure or object into a sequence of bits so that it can be stored in a file or memory buffer, or transmitted across a network connection link to be reconstructed later in the same or another computer environment. Design an algorithm to serialize and deserialize a binary tree. There is no restriction on how your serialization/deserialization algorithm should work. You just need to ensure that a binary tree can be serialized to a string and this string can be deserialized to the original tree structure.
Clarification: The input/output format is the same as how LeetCode serializes a binary tree. You do not necessarily need to follow this format, so please be creative and come up with different approaches yourself.
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
Things you should know
1. Mapping binary tree to list
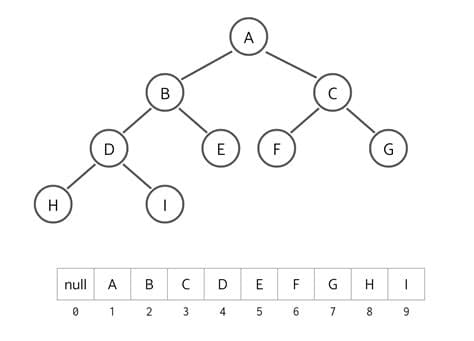 When mapping a binary tree to a list, you generally skip the first index (
When mapping a binary tree to a list, you generally skip the first index (0). This is done because it makes it easier to calculate the indices of parent and child nodes. Specifically, for a node at index i:- The left child is at index
2*i - The right child is at index
2*i + 1
Solutions
1. Using BFS
In this solution, we leverage the BFS algorithm to serialize and deserialize a binary tree. The deque from Python's collections module is used to efficiently manage the nodes during both processes. Below is the complete implementation:
Note that in my solution, empty nodes(literally nodes that do not exist) are serialized into the string #. You can choose whatever character you'd like.
class Codec:
def serialize(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> str:
# Initialize deque with root node.
queue = deque([root])
# 'result' has one dummy entry to skip the first index.
result = ['#']
# Perform BFS to serialize the tree.
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
if node:
# Append left and right children to the queue.
queue.append(node.left)
queue.append(node.right)
# Append current node value to the result.
result.append(str(node.val))
else:
# Append '#' to the result if the node is None.
result.append('#')
# Join all elements in the result list with a space and return as string.
return ' '.join(result)
def deserialize(self, data: str) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
# Edge case: if data is empty or only contains the root placeholder.
if not data or data == '# #':
return None
# Split the data string into a list of node values.
nodes = data.split()
# Initialize the root node with the value at index 1.
root = TreeNode(int(nodes[1]))
# Initialize a queue with the root node.
queue = deque([root])
# Start from index 2 since index 0 is a dummy and index 1 is the root.
index = 2
# Perform BFS to deserialize the tree.
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
# Process the left child.
if index < len(nodes) and nodes[index] != '#':
node.left = TreeNode(int(nodes[index]))
queue.append(node.left)
index += 1
# Process the right child.
if index < len(nodes) and nodes[index] != '#':
node.right = TreeNode(int(nodes[index]))
queue.append(node.right)
index += 1
# Return the reconstructed root node.
return root